Promotional Features
Organic DHA algae oil: Satisfying consumer demand for dietary supplements and environmental concerns
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid essential for brain development during pregnancy and early childhood. It has also been linked to improved heart health, vision, and reduced inflammatory responses. This long-chain fatty acid is found in cell membranes throughout the body and helps transmit messages between nerves.
Our bodies naturally produce DHA in small amounts, but to achieve adequate amounts, DHA needs to be consumed through dietary sources such as cold-water fish, grass-fed meat, dairy products, or omega-3-rich or pasture-raised eggs. According to an August 2021 article by the National Institutes of Health, a medical research organization, dietary intake of EPA and DHA contributes very little to total daily omega-3 intake (about 40 mg for children and adolescents and about 90 mg for adults). Therefore, the use of dietary supplements containing omega-3 fatty acids is essential.
According to Coherent Market Insights, the global DHA Supplements market is estimated to be valued at US$ 1,385.8 million in 2021 and is expected to exhibit a CAGR of 7.0% during the forecast period (2021-2028).[1]
However, global warming is predicted to reduce the de novo synthesis of DHA by algae under the aquatic food chain and is expected to reduce DHA transfer to fish. The rising water temperatures could lead to a loss of approximately 10% to 58% of globally available DHA by 2100, potentially limiting the human availability of this crucial nutrient. It is a general trend to seek other sources of DHA, and DHA algal oil is one of the options.[2]
CABIO DHA Algal Oil
CABIO is a biotechnology company that provides high-quality nutritional products for customers in the nutrition and health industry. All products are obtained through sustainable microbial fermentation. Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) oil is one of the leading products of the company, and it is produced by fermentation with an algal organism (Schizochytrium sp.), a strain approved by EFSA and FDA for industrial DHA production through microbial fermentation.
The Schizochytrium sp. strain with a high yield of DHA was obtained by a combination of ion beam injection mutagenesis and flow cytometry. According to the characteristics of fermentation and metabolism of Schizochytrium sp., we optimized the medium composition, formulated the fed-batch feeding strategy, and established the exemplary regulation method. With all these improvements, we finally obtained a strain with high and stable DHA yield and low consumption. At the same time, CABIO developed a green preparation technology for solvent-free extraction, and we adopted strict refining process control to ensure the increased safety and higher quality of DHA algal oil products.
Organic Market
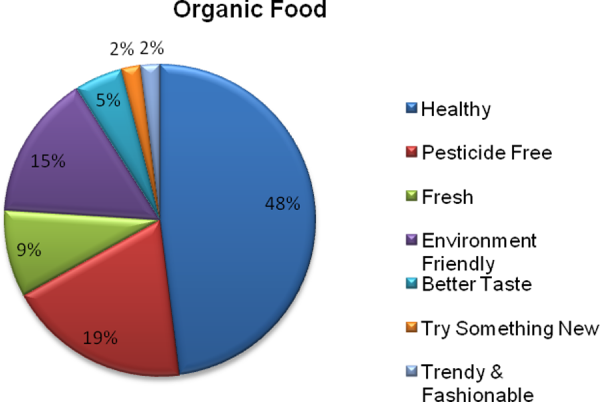
Foods that are cultivated without the application of chemical pesticides can be called organic foods. The feed cannot include antibiotics or growth hormones for the food products labeled organic for foods derived from animals (e.g., eggs, meat, milk, and milk products) [3].
Consumers perceive organic foods as more nutritious, natural, and environmentally friendly than non-organic or conventional foods. They are sensitive to the product, processing, and brand information that could impact the environment. Environmental issues are thought to have a more direct impact on the well-being of consumers. Consumers aware of ecological degradation activities are willing to buy organic food.
Increased healthy and environmental awareness and consumers' desire to buy organic food have led to increased investment by businesses in producing and marketing organic food.
Image source: https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0257288.g002
CABIO Organic DHA Algae Oil
National Organic Program (NOP) regulations allow organic products to be produced by fermentation. Based on the booming demand in the organic market, CABIO devotes itself to offering customers more choices of raw material types, including organic DHA algae oil.
The organic agriculture regulations are stringent on processes and materials used to process organic products. By restricting this requirement, the first concern is the fermentation process. The culture medium used must meet specific regulatory requirements, such as using organic glucose as a carbon source, organic yeast as a nitrogen source, and inorganic salts permitted by regulations. Therefore, searching for proper organic carbon and nitrogen sources has become the biggest obstacle to producing organic DHA algae oil. After all, there are few organic raw material suppliers, and the cost of organic raw materials is very high. At present, we have found several qualified organic raw material suppliers to guarantee the stability of the supply chain.
Meanwhile, CABIO has developed independent preparation of organic C and N sources from upstream agricultural products and set up an alternative method for replacing existing C and N sources with other medium materials uncommonly used. We did all these things to avoid the supply chain being affected by uncontrollable factors (epidemic, war, etc.) and keep the product cost under control.
Besides, according to the change of culture medium, CABIO has further optimized the fermentation process and adjusted the technical parameters such as culture medium concentration, dosage, feeding time, culture temperature, pH value, and oxygen solubility to ensure the high yield and content of DHA algal oil. Moreover, a new solvent-free refining line was built in addition to the existing solvent-free extraction line so that the oil refining process could meet the requirements of organic agricultural production. After a long time of exploration and testing, our organic DHA algal oil has strict compliance with the organic production requirements and has met the national standards for DHA algal oil. The DHA content in the algal oil is more than 35%, the moisture content is less than 0.05%, and the trans-fatty acid content is less than 1%.
On November 18th, 2020, CABIO received a notice from ECOCERT SA that "docosahexaenoic acid oil," "Aquatic plant seaweed," and "DHA algae oil" of CABIO had passed the ORGANIC certification in the United States.
Recently, there have been limited organic DHA algal oil suppliers worldwide due to high production costs and low product returns. CABIO provides high-quality and inexpensive organic DHA algae oil certified by USDA ORGANIC to meet the needs of more customers in the organic market.
CABIO provides customers with high-quality cosmetic ingredients, functional food ingredients, and other products through ion beam biotechnology, microbial breeding, fermentation engineering, synthetic biology, and other technical means. CABIO is a biotechnology-based company that combines targeted optimization of industrial strains, precisely regulated fermentation, and efficient separation and purification.
With biotechnology as our pillar, CABIO provides customers from the nutrition and health industry worldwide with quality nutrient products and innovative solutions through sustainable microorganism fermentation. CABIO has already cooperated with Cargill, Nestle, Danone, Abbott, Kerry, Givaudan, Feihe, Junlebao, Yili, By-Health, H&H Group, Angel Yeast, et cetera.
References:
[1] https://www.globenewswire.com/news-release/2022/05/10/2439788/0/en/Global-DHA-Supplements-Market-to-Surpass-US-2-237-9-Million-by-2028-Says-Coherent-Market-Insights-CMI.html
[2] Colombo, S.M., Rodgers, T.F.M., Diamond, M.L. et al. Projected declines in global DHA availability for human consumption as a result of global warming. Ambio 49, 865–880 (2020).
[3] https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0257288